| Absorption | Adsorption |
|---|---|
| It is the phenomenon in which the particles of gas or liquid get uniformly distributed throughout the body of the solid. | It is the phenomenon of higher concentration of particles of gas or liquid on the surface than in the bulk of the solid. |
| The concentration is the same throughout the material. Therefore, it is a bulk phenomenon. | The concentration on the surface of the adsorbent is different from that in the bulk. Therefore, it is a surface phenomenon. |
| Absorption occurs at uniform rate. | Adsorption is rapid in the beginning and its rate slowly decreases. |
| It is an endothermic process. | It is an exothermic process. |
| Example – anhydrous calcium chloride absorbs water. | Example – silica gel adsorbs water vapours. |
Tuesday, 13 March 2018
Absorption Vs Adsorption
Monday, 12 March 2018
Open Word Class Vs Closed Word Class
| Open Word Class | Closed Word Class |
|---|---|
| 1. An open class is one that commonly accepts the addition of new words. | 1. A closed class is one that contains fixed number of words. |
| 2. Open class of words is also called content words. | 2. Closed class of words is also called function words. |
| 3. This class contains large number of words. | 3. This class contains limited number of words. |
| 4. New words are generally coined or borrowed from other languages. | 4. No new words are added. |
| 5. This class consists of nouns, verbs, adjectives and adverbs. | 5. This class consists of pronouns, articles and prepositions. |
Sunday, 11 March 2018
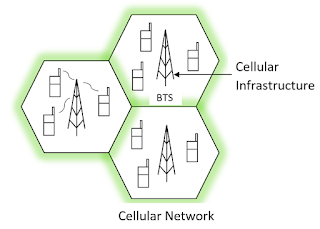
Ad Hoc Networks Vs Cellular Networks
| Ad Hoc Networks | Cellular Networks |
|---|---|
| Ad Hoc network is a type of multi-hop wireless networks i.e. a collection of nodes that communicate with each other wirelessly by using radio signals over a shared common channel. | A cellular network is a radio network distributed over land through cells where each cell includes a fixed location transceiver known as base station. |
|
|
|
| Infrastructure less network. | Infrastructured network. |
| No base station and rapid deployment. | Fixed pre-located cell sites and base station. |
| Highly dynamic network topology. | Static backbone network topology. |
| Multi-hop wireless links. | Single hop wireless links. |
| Packet switching is used. | Circuit switching is used. |
| Mesh topology is used. | Star topology is used. |
| Irregular connectivity. | Stable connectivity. |
| Cost-effective. | High setup cost. |
| Less setup time. | Large setup time. |
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)